LLM Security
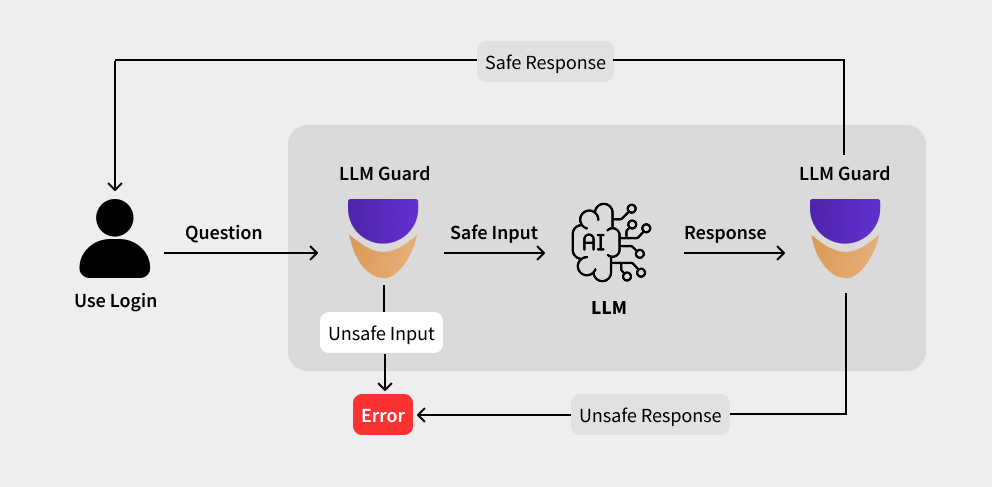
LLM Guard
The Security Toolkit for LLM Interactions
- LLM Guard by Protect AI is a comprehensive tool designed to fortify the security of Large Language Models (LLMs).
- By offering sanitization, detection of harmful language, prevention of data leakage, and resistance against prompt injection attacks, LLM-Guard ensures that your interactions with LLMs remain safe and secure.
LLM Guard secures large language model (LLM) interactions by routing all inputs and outputs through a dedicated sandbox. Within this controlled environment, every piece of data is scrutinized for risks—ranging from prompt injection and adversarial manipulations to jailbreak techniques and inadvertent PII exposure—before it reaches the live model.

Key Attack Vectors

1. Prompt Injection
Malicious inputs may overwrite or bypass safe instructions, potentially triggering the model to reveal sensitive information.
2. Adversarial Inputs
Slight alterations in phrasing or formatting can bypass basic filters, risking unintended disclosure of confidential data.
3. Jailbreak Techniques
Carefully crafted prompts might disable built-in safeguards, leading to the exposure of PII or other sensitive content.
4. Context Manipulation
Chained or complex input sequences can drive the model into unsafe operational states.
Sandbox-Based Security Mitigation and Real Output Scoring Evaluation
Input Sanitization & Output Verification:
- Each scanner (for example, those designed for PII redaction, prompt injection detection, or content quality assessment) processes the data and returns a risk score between 0 (no risk) and 1 (high risk), along with a validity flag.
Output Scoring Evaluation:
- Individual Scoring: Each output scanner evaluates the model’s response by calculating a risk score based on its specific criteria. For instance, the Sensitive Scanner might score an output at 0.2 if minimal PII is detected, while a Prompt Injection Scanner could score a higher risk if hidden instructions are uncovered.
- Aggregation: The sandbox aggregates these individual risk scores—using methods such as weighted averaging or threshold-based scoring—to produce an overall risk evaluation for the output.
- Decision Making:
- If the aggregated risk score falls below a predefined threshold (e.g., 0.5), the output is deemed safe and allowed to pass through.
- If the score exceeds this threshold, the system either automatically redacts sensitive content, flags the output for review, or rejects the response entirely.
- Continuous Feedback: This real output scoring evaluation not only provides immediate quantifiable feedback on the safety of the output but also feeds into ongoing model and scanner refinements, ensuring that emerging threats are promptly addressed.
Conclusion
By combining sandbox isolation, rigorous input/output scanning, and a robust real output scoring evaluation mechanism, LLM Guard ensures that only data meeting strict safety criteria reaches the live model. This multi-layered approach protects against sophisticated adversarial attacks and inadvertent PII leaks, while the detailed risk scores allow security teams to make informed decisions about the integrity of each interaction.
